
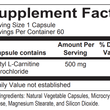
Acetyl L-Carnitine
Acetyl L-carnitine has been used in clinical trials and has shown positive effects on cognitive function and nerve and cardiovascular health.
CLINICAL APPLICATIONS
- Supports Cognitive Function, Memory and Mood Health
- Promotes Cardiovascular Health
- Supports Nerve Health
- Improves Cellular Energy
OVERVIEW
Acetyl L-carnitine (ALC) is an ester of the trimethylated amino acid, L-carnitine, and is synthesized in the human brain, liver, and kidney by the enzyme ALC transferase. Acetyl L-carnitine transports long chain fatty acids across mitochondrial membranes into the mitochondria, where they are burned as fuel and produce cellular energy known as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Acetyl L-carnitine also transports small chain fatty acids out of the mitochondria, helping to maintain coenzyme A levels crucial for maintaining the energy production cycle. In brain health, zcetyl L-carnitine plays a role in the formation of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter (brain chemical), which is essential to the processes of learning and concentration. Research has found that ALC particularly beneficial in cognitive health, supporting mood in the elderly and promoting nerve and cardiovascular health.
A modified form of the amino acid L-Carnitine, ALC has been shown to have distinct cognitive benefits from the non-acetylated form, namely enhancing production of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. ALC benefits mood health and supports brain function. Studies have shown that ALC also supports nerve and cardiovascular health by supporting metabolism and boosting energy production within the cells’ mitochondria. Each capsule of Acetyl L-Carnitine includes 500 mg of acetyl L-carnitine for maximum support.
Suggested Use
1 capsule per day or as recommended by your health care professional
INGREDIENT BENEFITS
Acetyl L-Carnitine
Acetyl L-Carnitine has been used in clinical trials, which have shown positive effects on cognitive function. A modified form of L-Carnitine, acetylated L-Carnitine is believed to have cognitive benefits distinct from the non-acetylated form.


